Understanding SSL Certificates
In this article you will get to know about the following things:
What is an SSL certificate?
SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layers. It is a digital certificate or guarantee of a safe and encrypted connection which gives the confidence to the user that he could share his personal information with the website. An SSL certificate authenticate a websites identity. It is also known as TLS transport layer security.
One of the most important components of an online business is to establish a trust between the potential users and the website, an SSL certificate plays a key role in doing so. Online appearances of companies and organizations which are their websites need an SSL in order to protect their customer’s data and to avoid it from going into bad hands. In short, an SSL certificate secure and prevents unauthorized users from reading or modifying the confidential data. By data we are referring to a vast scope of info which may include usernames their addresses, contact information or even financial details like credit card numbers as well.
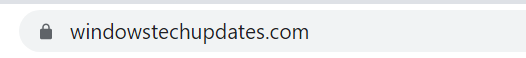
How does SSL work?
The data transfer/exchange between a web-server and client(browser) taking place in the presence of an SSL is called an SSL handshake. The data is first encrypted and then transferred so that any middle man could not read it. This encryption process is done with the help of public, private and session keys. The process is explained as follows:
- The browser connects with the web-server(website) and requests the web-server identifies itself.
- Server a sends a copy of its SSL certificate to the browser including the server’s public key.
- The browser checks the SSL certificate by checking its roots among a list of trusted CA’s (Certificate Authority) and also checks its expiry and then if it is good, browser signals the web-server.
- The web-server then sends a digitally signed acknowledgement and decrypts the session key using its private key.
- A secure and encrypted connection is developed between the browser and the website.
How to check if a site has SSL or not?
The easiest way to check whether a site is secure or not is by:
- Firstly, looking at its URL, if it has HTTPS (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secured) instead of HTTP it means that it has a SSL certificate and is safe to use and give credential information.
- Secondly, if it has a closed padlock on the left of its URL. It is indication of a SSL certificate.
For non-secure websites your browser may give a warning also that they don’t have padlock or there is a red triangle there for a website not secured by SSL.
Most secured and safe websites have a green padlock.

Types of SSL certificate
It is essential to be familiar with the different types of SSL certificates to obtain the right type of certificate for your website.
Currently there are six (6) types of SSL’s categorized depending upon their validation levels:
- Extended Validation certificates (EV SSL)
- Organization Validated certificates (OV SSL)
- Domain Validated certificates (DV SSL)
- Wildcard SSL certificates
- Multi-Domain SSL certificates (MDC)
- Unified Communications Certificates (UCC)
Extended Validation Certificate (EV SSL)
It is the safest and the most expensive SSL. To set up an EV SSL certificate, the website owner must go through a standardized identity verification process to confirm they are authorized legally to the exclusive rights to the domain.
They are most used by high-profile websites such as banks, government organizations etc.
Organization Validated Certificate (OV SSL)
These are the second most expensive certificates. The Organization Validation SSL certificate’s primary purpose is to encrypt sensitive information during transactions. The OV certificate has a high assurance, similar to the EV certificate, and is also used to validate business credibility.
Domain Validated Certificate (DV SSL)
As DV certificates are one of the least expensive and fastest types to obtain, they are often used by blogs or informational websites that don’t need to provide extra assurance to their visitors.
Compared to other SSLs, Domain Validation SSL certificates have low assurance and minimal encryption. Hence, the validation process to obtain this certificate type is minimal. The process only requires website owners to prove domain ownership by responding to an email or phone call.
Wildcard SSL Certificates
Wildcard SSL certificates allow you to secure a base domain and unlimited sub-domains on a single certificate. If you have multiple sub-domains to secure, then a Wildcard SSL certificate purchase is much less expensive than buying individual SSL certificates for each of them. For example:
- payments.yourdomain.com
- login.yourdomain.com
- mail.yourdomain.com
- download.yourdomain.com
Multi-Domain SSL (MDC)
Multi-Domain SSL certificates can secure many different domain names and subdomains using a single certificate, which helps save time and money. This includes the combination of completely unique domains and sub-domains with different TLDs (Top-Level Domains) except for local/internal ones. For example:
- www.example.com
- example.org
- mail.this-domain.net
- example.anything.com.au
- checkout.example.com
Unified Communication Certificates (UCC)
Unified Communications Certificates (UCC) are also considered Multi-Domain SSL Certificates and have the same benefits. Today, any website owner can use these certificates to allow multiple domain names to be secured on a single certificate. UCC Certificates are organizationally validated and display a padlock on a browser.
How to get a new SSL?
You can get a new SSL from a CA (certificate authority). CA’s gives hundreds of thousands of SSL’s every year. A CA is an outside organization, a trusted third party, that generates and gives out SSL certificates. The CA will also digitally sign the certificate with their own private key, allowing client devices to verify it. It could cost you from free to hundreds of dollars depending upon what level of security you are demanding for. The time to issue SSL also depends on which type of SSL you are getting.
SSL Expiry
Any SSL certificate is not forever. It has an expiry date after it has to be renewed by a CA.
Find more related articles like fixing SSL/TLS vulnerabilities.
HTTPS doesn’t mean that website is safe and secure. SSL certificate can be issued from non-trusted authority or even self signed. SSL Certificate only tells that website has identity information. In order to trust a website, green padlock guarantees that SSL certificate is issued from trusted CA. User can then communicate with that website with confidence that his / her information will travel over secure communication channel.
Thanks @Israr Ahmad for sharing this wonderful information, every comment is really important for use to improve our content.